A review of the scientific literature on the Mediterranean Diet and Diabetes risk and prevention
The sad truth is that most of us know someone who has diabetes. Diabetes is a growing chronic disease that is negatively impacting lives worldwide. Currently, there is no cure for diabetes, though there are therapeutic options such as insulin injections that diabetic patients can resort to. To be clear, diabetes is disease condition in which glucose molecules are not being taken up by the human body cells, and thus are not being broken down for energy. This results in a lack of energy and glucose in the cells, and high levels of glucose in the blood—this is not safe for the human body, as it can lead to several complications such as kidney failure or blindness. So, you can imagine that diabetic patients need to keep their blood glucose levels down and stick to a healthy diet.
BUT what is glucose and where does it come from?…Well, glucose is basically the most broken down form of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are made up of glucose molecules, for instance maltose is a disaccharide, made up of two glucose molecules. Multiple different maltose molecules can combine to form a large chain, which then forms carbohydrates. You may be wondering which foods contain carbohydrates. Almost all foods contain carbohydrates, from ice cream to bananas. However, the following is a list of foods with amounts of carbohydrates:
Now, you all may be wondering if there is an easy diet that dan be followed to reduce the level of glucose consumed. Going on a strict carbohydrate-free diet can be tough, stringent, and demanding, thus, it is important for patients with diabetes to resort to a diet that is easy to follow and is effective. Luckily, I will be discussing the Mediterranean diet, which I will be referring to as “MD”.
The MD has been along for centuries. It is a traditional diet consumed by several countries along the Mediterranean Sea. The MD consists largely of colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, fish and seafood, olive oil, and red wine. However, this diet extends beyond food, it also involves and active lifestyle, and spending time with family and friends when consuming meals. The MD looks something like following:
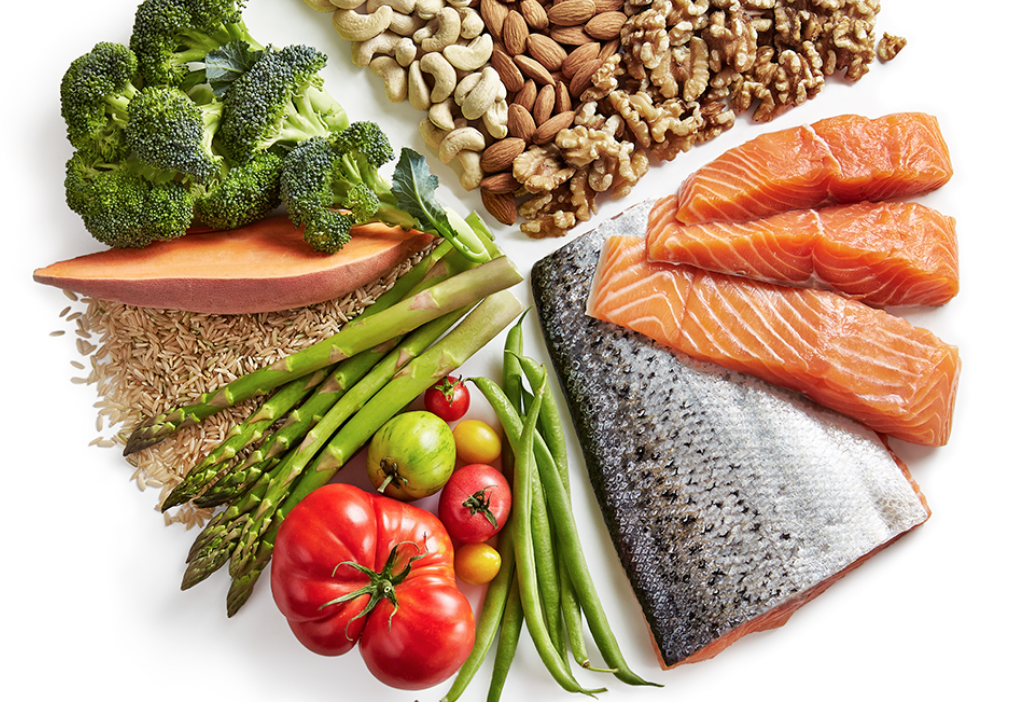

This diet is not only delicious and appetizing, but it is also very healthy and beneficial for diabetic patients. This is because it consists of fruits and vegetables with every meal, includes whole grains, such as quinoa, seafood and nuts, which contain very beneficial fats. These foods are very healthy if consume regularly for several physiological and biological reasons. Diabetes can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol, inflammation, and heart diseases; thus, it is essential to consume foods that could combat these complications (Benson et al., 2011). The MD contains several fishes and nuts; these foods contain plenty of omega 3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are very healthy because they lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol. This reduces the risk of plaque building and clogged-arteries which reduces the risk of heart disease. This is beneficial for diabetic patients because having a high source of health unsaturated fats can maintain fat and cholesterol levels, and this can also be used as energy instead of high amounts of glucose molecules (Lee et al., 2016). The MD also contains a glass of wine per day. Wine has been shown to be healthy because it reduces lipid peroxidation, which is a form of inflammation. This is very beneficial because inflammation in diabetic patients can lead to heart issues and atherosclerosis (Gorelik et al., 2008).
According to several studies, the MD is beneficial because it improves glycemic control, which means it enhances the uptake of glucose by the cells, which can then break it down and use it as energy. The diet also lowers the amount of sugar in our bodies. This is because the MD consists of very little carbohydrates, and even then, the carbohydrates are complex. This is healthy because the body breaks down these carbohydrates slowly, which allows the body to slowly uptake the glucose from the body because the insulin is very sensitive (Shai et al., 2008).
Furthermore, the MD is very beneficial for diabetic because it also reduces BMI, waist-to-hip ratio, and metabolic syndrome. Studies have shown the high protein from the fish and the healthy complex carbohydrates aids with digestion and weight loss (Esposito et al., 2010). This is very important for diabetic patients because when glucose is not being consumed for energy, the body may resort to overeating for carbohydrates and thus energy. Additionally, according to several studies, the MD is very beneficial because it prevents diabetes. Around 83% of individuals in a study had a lowered risk of diabetes after sticking to the MD (Martínez-González et al., 2008). MD was also shown to reduce the risk of diabetes in patients with cardiovascular diseases. A lot of this is because of the health fats found in olive oil, nuts, and fish. These fats are known as unsaturated fats, as opposed to saturated fats. These fats, along with fruits and vegetables, help improve systolic and diastolic blood pressure, lower inflammation, and studies have shown that they also prevent the onset of diabetes (Risérus et al., 2009).

References
Ohnishi, M., Leshabari, S., Ambikile, J. S., Oishi, K., Nakao, Y., & Nishihara, M. (2017). Associations among anthropometric measures, food consumption, and quality of life in school-age children in Tanzania. Journal of Rural Medicine,12(1), 38-45. doi:10.2185/jrm.2924
Lifer, H. S. (n.d.). Lose Weight, Live Longer With Mediterranean Zone Diet – Barry Sears. Retrieved April 29, 2019, from https://www.aarp.org/health/healthy-living/info-2014/mediterranean-zone-diet.html
Cholesterol Levels: What the Numbers Mean. (n.d.). Retrieved April 29, 2019, from https://www.medicinenet.com/cholesterol_levels_pictures_slideshow/article.htm
Gorelik S, Ligumsky M, Kohen R, Kanner J: The stomach as a “bioreactor”: when red meat meets red wine. J Agric Food Chem 56:5002–5007, 2008
Shai I, Schwarzfuchs D, Henkin Y, Shahar DR, Witkow S, Greenberg I, Golan R, Fraser D, Bolotin A, Vardi H, Tangi-Rozental O, Zuk-Ramot R, Sarusi B, Brickner D, Schwartz Z, Sheiner E, Marko R, Katorza E, Thiery J, Fiedler GM, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Stampfer MJ; Dietary Intervention Randomized Controlled Trial (DIRECT) Group: Weight loss with a low-carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or low-fat diet. N Engl J Med 359:229–241, 2008
Esposito K, Maiorino MI, Ceriello A, Giugliano D: Prevention and control of type 2 diabetes by Mediterranean diet: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 89:97–102, 2010
Martínez-González MA, de la FuenteArrillaga C, Nunez-Cordoba JM, Basterra-Gortari FJ, Beunza JJ, Vazquez Z, Benito S, Tortosa A, Bes-Rastrollo M: Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of developing diabetes: prospective cohort study. BMJ 336:1348–1351, 2008
Risérus U, Willett WC, Hu FB: Dietary fats and prevention of type 2 diabetes. Prog Lipid Res 48:44–51, 2009
11 Proven Benefits of Olive Oil. (n.d.). Retrieved April 28, 2019, from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-proven-benefits-of-olive-oil










